Architecture¶
Architecture overview¶
MaxwellLink separates electromagnetic propagation from molecular dynamics by placing them in different processes (or even different nodes) and letting them communicate through a socket protocol, inspired by the i-PI project:
The EM solver (such as Meep FDTD or single-mode cavity) advances Maxwell’s equations.
After each time step, MaxwellLink measures the regularized electric field at every coupled molecule and converts it to atomic units.
Those field vectors are sent to the driver processes through a
SocketHubbarrier call.Each driver propagates its molecular model for one EM step (possibly using sub-steps) and returns the time-derivative of the dipole moment and optional metadata.
The returned amplitudes are converted back to EM units and injected to EM solvers before the next time step begins.
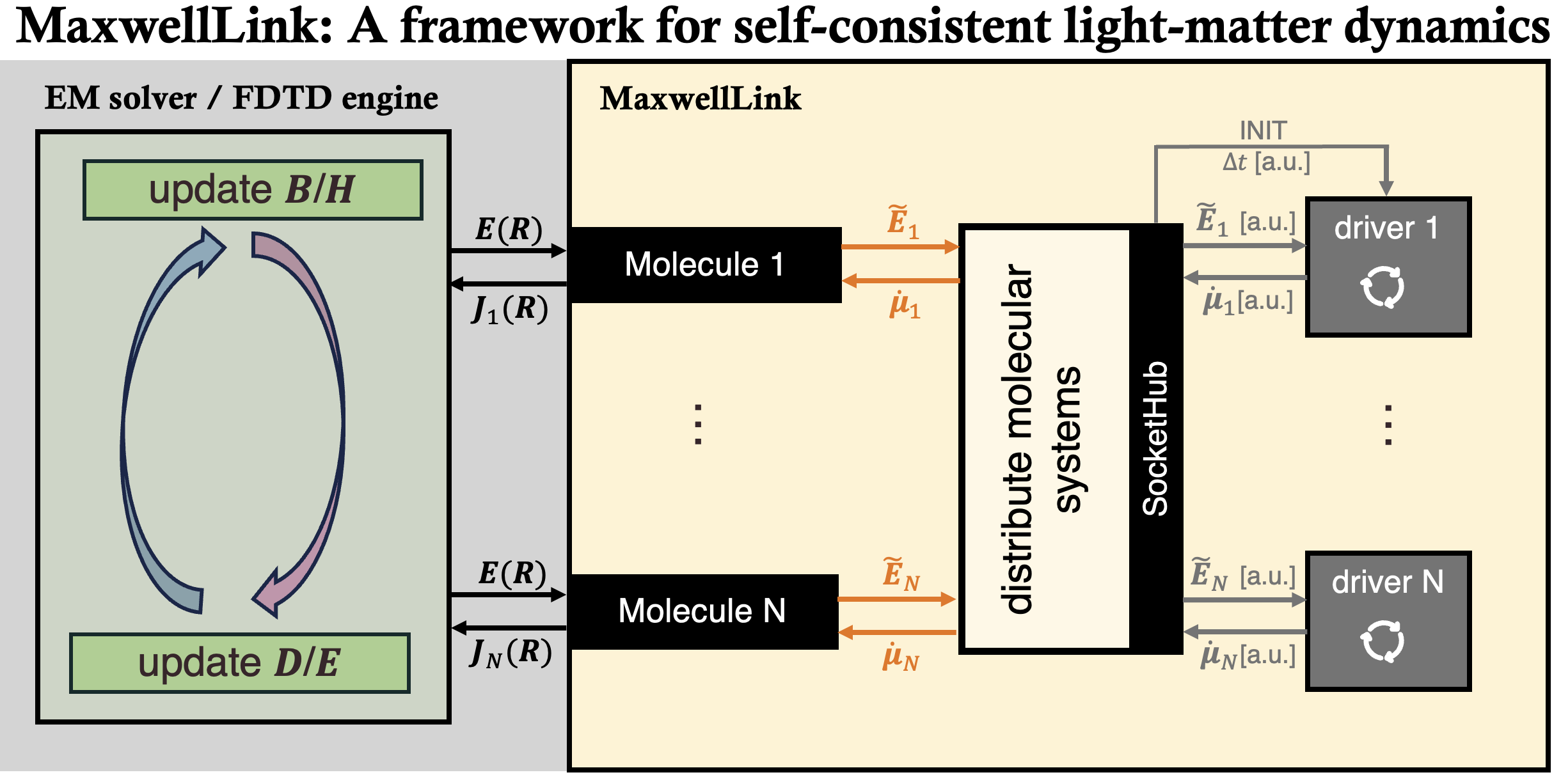
SocketHub¶
SocketHub (maxwelllink.sockets.sockets) manages the inter-code communication:
Supports both TCP sockets (
host/port) and UNIX domain sockets (unixsocket).Generates molecule IDs on demand.
Implements the
NEEDINIT -> INIT -> READY/HAVEDATAhandshake for each client.Detects dropped connections during sends or receives and pauses the EM solver until all expected drivers reconnect.
Exposes helpers such as
maxwelllink.sockets.sockets.get_available_host_port()for easy use.
Abstract Molecule¶
Molecule (maxwelllink.molecule.molecule) provides a unified interface for constructing molecular
drivers for both socket communications and non-socket (single-process) runs. Pass
hub=SocketHub(...) to connect to an external driver, or driver="..." (and
driver_kwargs) to instantiate the model locally.
Every molecule records time-resolved data in Molecule.additional_data_history (a Python list of dicts ordered in the simulation time).
For faciliating obtaining molecular time-resolved data, Molecule.extra is a dict that stores the post-processed data in the form of Numpy arrays.
The content of extra is determined by the driver implementation; for example, the TLS driver stores the population trajectory in extra["Pe"] and the time points in extra["time_au"].
In Molecule, each molecule only stores the information necessary for
EM simulations, such as the center / size of the molecule in the EM grid and the
Gaussian width (sigma) for molecular polarization density distribution. The detailed
molecular parameters and dynamics are handled by each driver implementation.
EM solvers¶
Currently, three EM solvers are available in MaxwellLink:
The Meep FDTD engine:
MeepSimulation(maxwelllink.em_solvers.meep)The single-mode cavity solver:
SingleModeSimulation(maxwelllink.em_solvers.single_mode_cavity).The laser-driven dynamics solver:
LaserDrivenSimulation(maxwelllink.em_solvers.laser_driven).
MeepSimulation derives from meep.Simulation and automatically
inserts the appropriate step function for updating molecules when MeepSimulation.run() is called.
When using MeepSimulation, three additional parameters should be specified compared to a regular
meep.Simulation:
molecules: a list ofMoleculeobjects to couple to the EM solver.time_units_fs: the mapping between Meep time units and real time in femtoseconds. Meep uses dimensionless units internally, so specifying this parameter is necessary to convert between Meep units and other units systems.hub: an optionalSocketHubobject for socket-based drivers.
Note
With a SocketHub a step function maxwelllink.em_solvers.meep.update_molecules() is inserted in Meep FDTD simulation;
without a hub the step function falls back to maxwelllink.em_solvers.meep.update_molecules_no_socket().
SingleModeSimulation, defined in SingleModeSimulation,
approximates the field as a single damped harmonic oscillator evolving in atomic
units. It supports the same socket and non-socket molecule interfaces, making it
useful for rapid prototyping or unit tests without launching Meep.
LaserDrivenSimulation, defined in LaserDrivenSimulation,
applies user-defined classical electric fields to molecules without back-action from the molecular system.
Please read EM Solvers section for detailed definitions of different EM solvers.
Molecular drivers¶
While Molecule defines molecular locations and size in EM grid, a set of molecular
drivers implement the actual dynamics. All Python-based drivers inherit from maxwelllink.mxl_drivers.python.models.dummy_model.DummyModel()
and use the unified API when communicating with the hub. The following Python drivers ship with MaxwellLink:
Two-level system (tls): a lightweight quantum model that propagates the von Neumann equation for a TLS.
QuTiP model Hamiltonians (qutip): an interface to user-defined Hamiltonians using the QuTiP package.
Psi4 RT-TDDFT (rttddft): real-time time-dependent density functional theory implemented using Psi4.
Psi4 RT-Ehrenfest dynamics (rtehrenfest): RT-TDDFT with nuclear Ehrenfest dynamics using Psi4.
ASE molecular mechanics (ase): first-principles Born-Oppenheimer molecular dynamics using the Atomic Simulation Environment (ASE).
An additional C++ LAMMPS driver implements fix mxl, which communicates with the hub
using the same socket protocol. See Installation for instructions on building
the LAMMPS binary with MaxwellLink support.
Please read Drivers section for detailed definitions of different molecular drivers.
MPI Parallelism¶
EM solvers, such as Meep FDTD, can be launched under MPI. MaxwellLink is compatible with MPI,
allowing for distributed simulations. Only the master
rank (rank 0) interacts with sockets; field integrals and returned molecule responses
are broadcast to the other ranks via mpi4py.
Checkpointing¶
Driver classes that inherit from DummyModel
support checkpointing. When checkpoint=true the driver writes state files
after each step; setting restart=true lets a reconnected driver resume from
disk. The hub blocks the EM solver inside wait_until_bound until all
expected molecules report back, so even long-lived RT-TDDFT simulations remain
consistent if a driver is restarted.